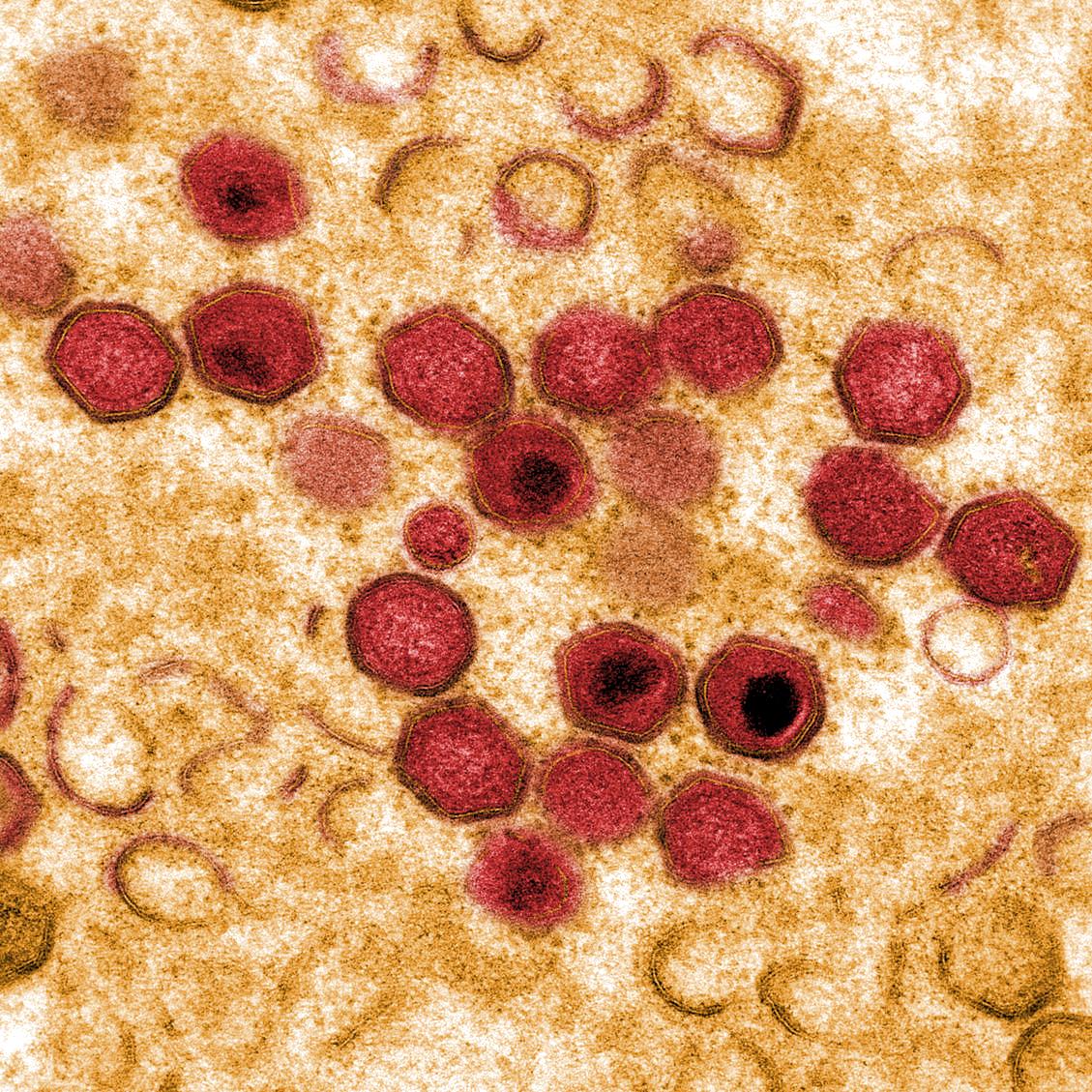
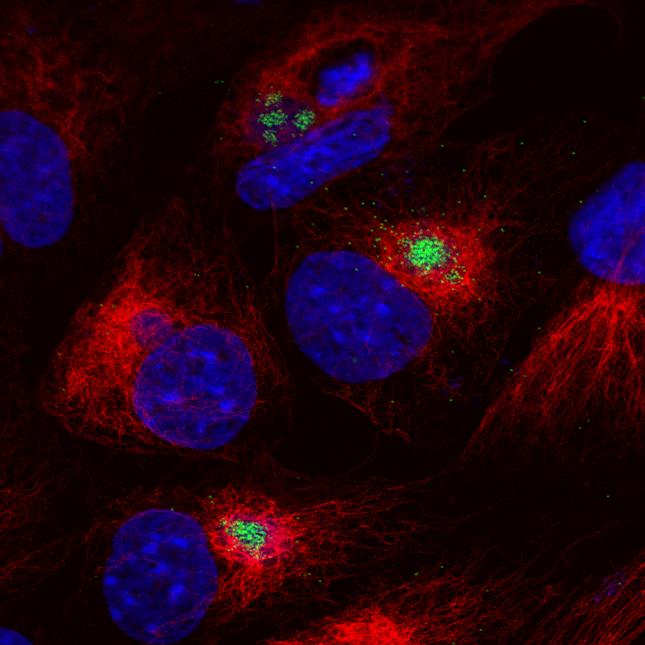
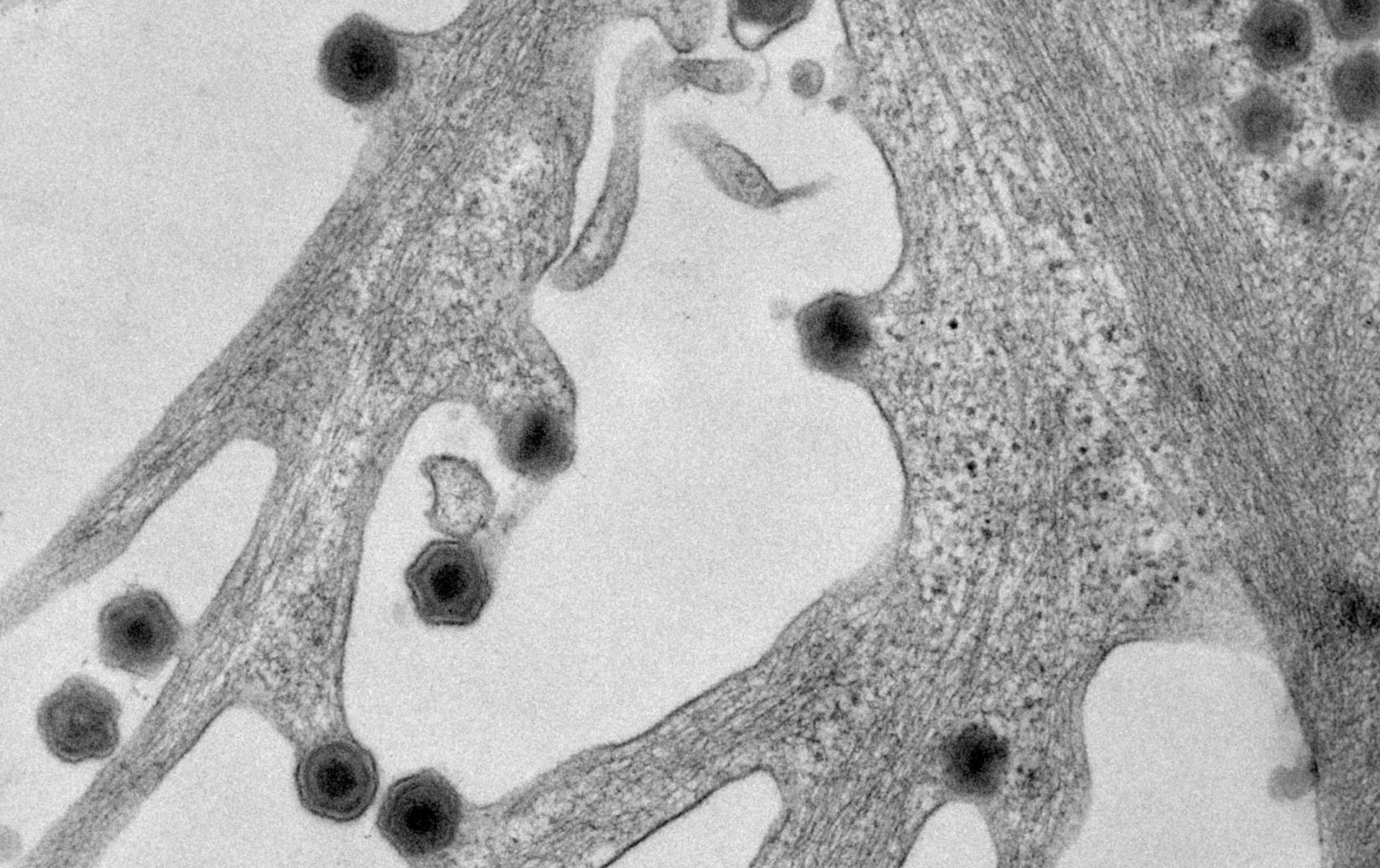
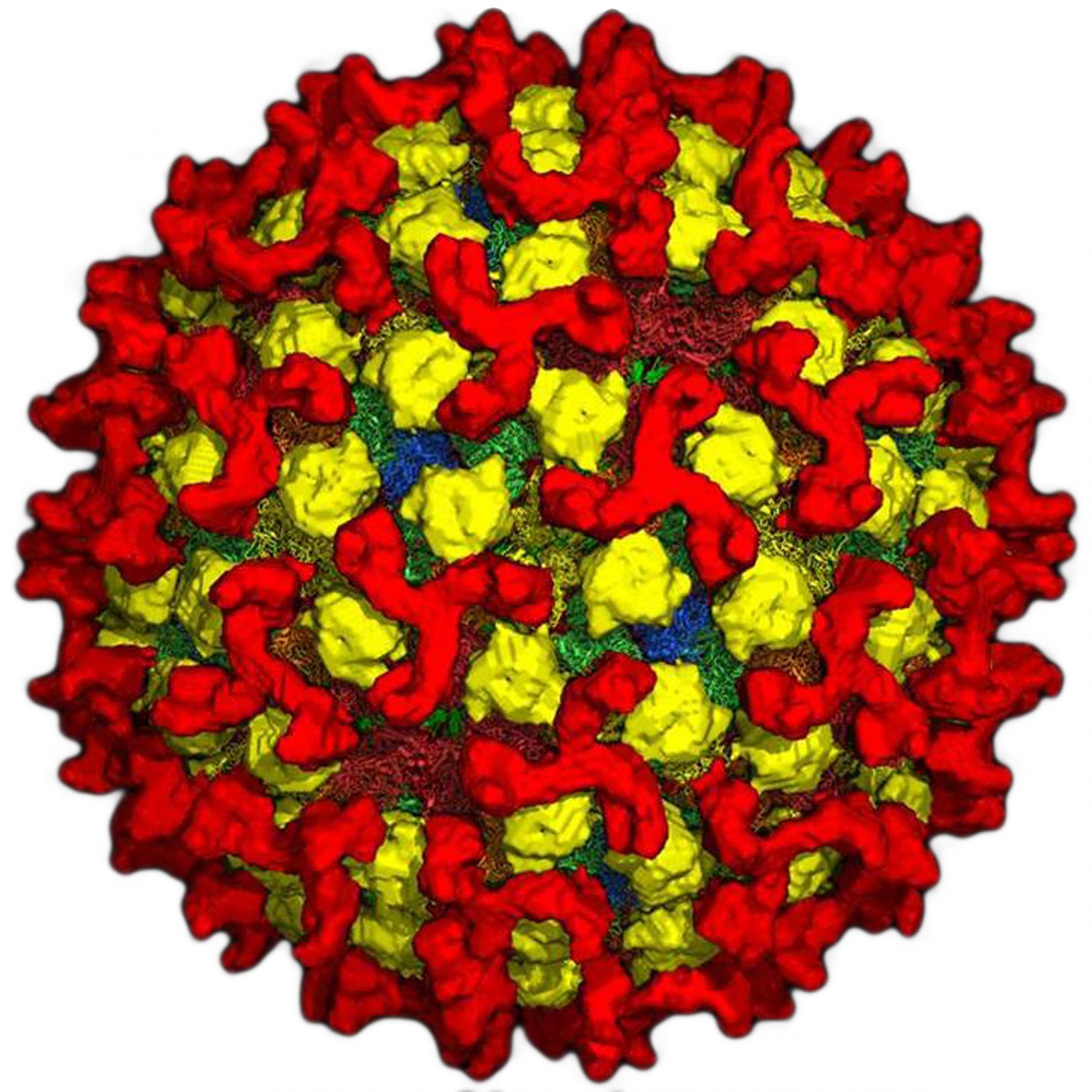
African swine fever (ASF) is a contagious disease that can be fatal for all infected domestic pigs and wild boar.
Pigs are usually infected through direct contact with other infected pigs, or indirectly by eating infected meat or meat products. The African swine fever virus (ASFV) can also be spread by soft ticks and through contaminated objects such as vehicles, clothes and equipment.
ASF is now prevalent in many countries in Europe, Asia and Africa. Originally found throughout sub-Saharan Africa, the virus was first introduced to Europe in 1957, but was eradicated from the continent, with exception of Sardinia, by the mid-1990s.
However, a second outbreak in 2007 led to the virus spreading across Eastern and Central Europe and much of Southern and Eastern Asia. Outbreaks have also occurred in Papua New Guinea and the Caribbean island of Hispaniola.
There has never been an outbreak of ASFV in the UK, and ASFV-free countries in Western Europe have strict policies in place to prevent infected live animals and pork products being imported.
Feeding pigs with swill, which contains human food waste, is banned in the UK and EU to prevent contamination. However, swill feeding remains common elsewhere, especially among smallholders.
Eliminating ASF is challenging due to the stability of the virus. In countries where ASFV is persistent, large numbers of wild pigs roam freely and can easily infect domestic pigs.
With such a high mortality rate, the disease is a significant animal welfare concern and severely impacts smallholders. ASF has a huge social and economic impact, costing hundreds of millions of pounds in affected countries. It can also be devastating for national economies, potentially incurring years of international trade bans on live pigs or pork meat products.
The presence of the disease in India, Bhutan, The Philippines and Indonesia means that ASF is now a huge conservation issue as critically endangered wild swine inhabit these parts of the world.
There is no treatment or vaccine available for ASFV. Measures to control the disease rely on effective surveillance, rapid diagnosis and movement restrictions. Control of ASFV can be particularly difficult among smallholders in lower income countries, where access to diagnostic tools and veterinary services can be limited.
Please see the Defra website for advice on how to spot and report the disease. Guidance to pig keepers on preventing the disease is also available.
Clinical signs
The clinical signs of ASF can vary but are similar to some other pig diseases. Signs typically occur 3-15 days after infection.
The early signs are non-specific and include:
- High fever, lethargy, and loss of appetite
- Pigs may die suddenly without further disease signs
At later stages, further signs may be observed including:
- Reddening of the skin (visible only in pale-skinned pigs), with patches appearing on the tips of ears, tail, feet, chest, or under the belly
- Diarrhoea, vomiting
- Laboured breathing
- Swollen red eyes, eye discharge
- Abortions, still-births
- Increasing morbidity and unwillingness to get up
In severe cases, death can sometimes be the only sign of infection, with a case fatality rate as high as 100%
Virology
ASFV is a large complex DNA virus and is the only member of the Asfarviridae family, genus Asfivirus. ASFV has several layers that surround a dense core containing its DNA genome. There are at least 23 genotypes.
Pirbright's research on African swine fever
Scientists at The Pirbright Institute have been working on understanding the virus since the 1960s.
Their expertise on how the virus works and how it interacts with the porcine (pig) immune system is crucial to the Institute’s vaccine development research.
Pirbright researchers are currently developing different types of ASF vaccines with the aim of producing one that will protect pigs from this deadly disease.
As the World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH) Reference Laboratory for ASF, Pirbright provides surveillance and diagnosis of ASF globally and continually works towards improving tests to detect the virus. Pirbright experts also provide advice to Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs (Defra) and WOAH, and have helped to provide resources for vets that will help them to identify ASF quickly should it ever present in the UK.
Resources
- For up to date information on the location of ASF outbreaks, visit the WOAH Information Database.
- Veterinary resource: ASF clinical signs
- Communication tools on ASF. Developed jointly by the WOAH and FAO as part of the “ASF kills pigs” campaign the materials are available in English, French, Spanish, Russian and Chinese and include messages targeted at key stakeholders (veterinarians, pig farmers and decision-makers) on actions they can take to prevent and control ASF.
- The WOAH's ASF information
- The FAO's most recent ASF updates