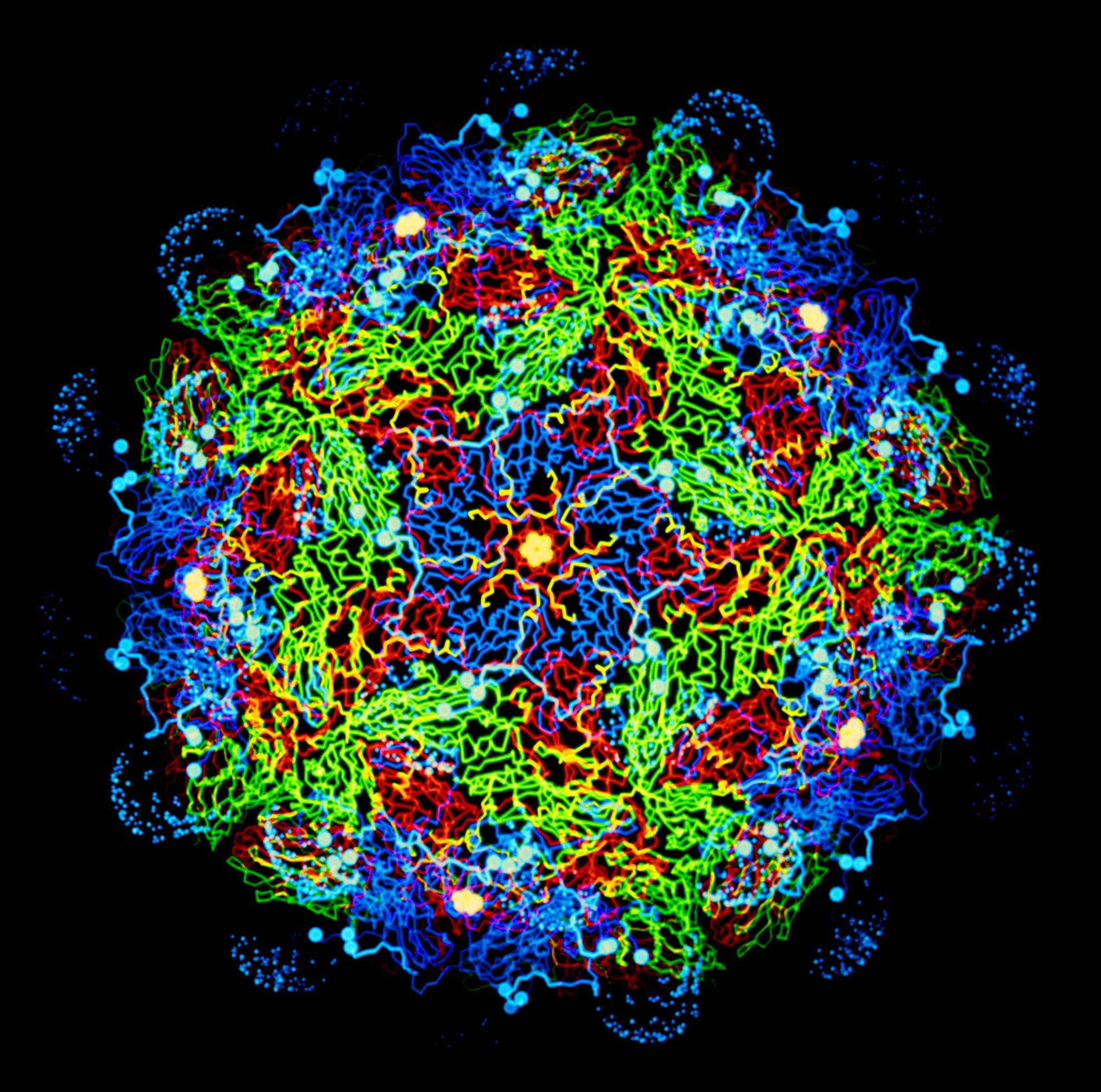
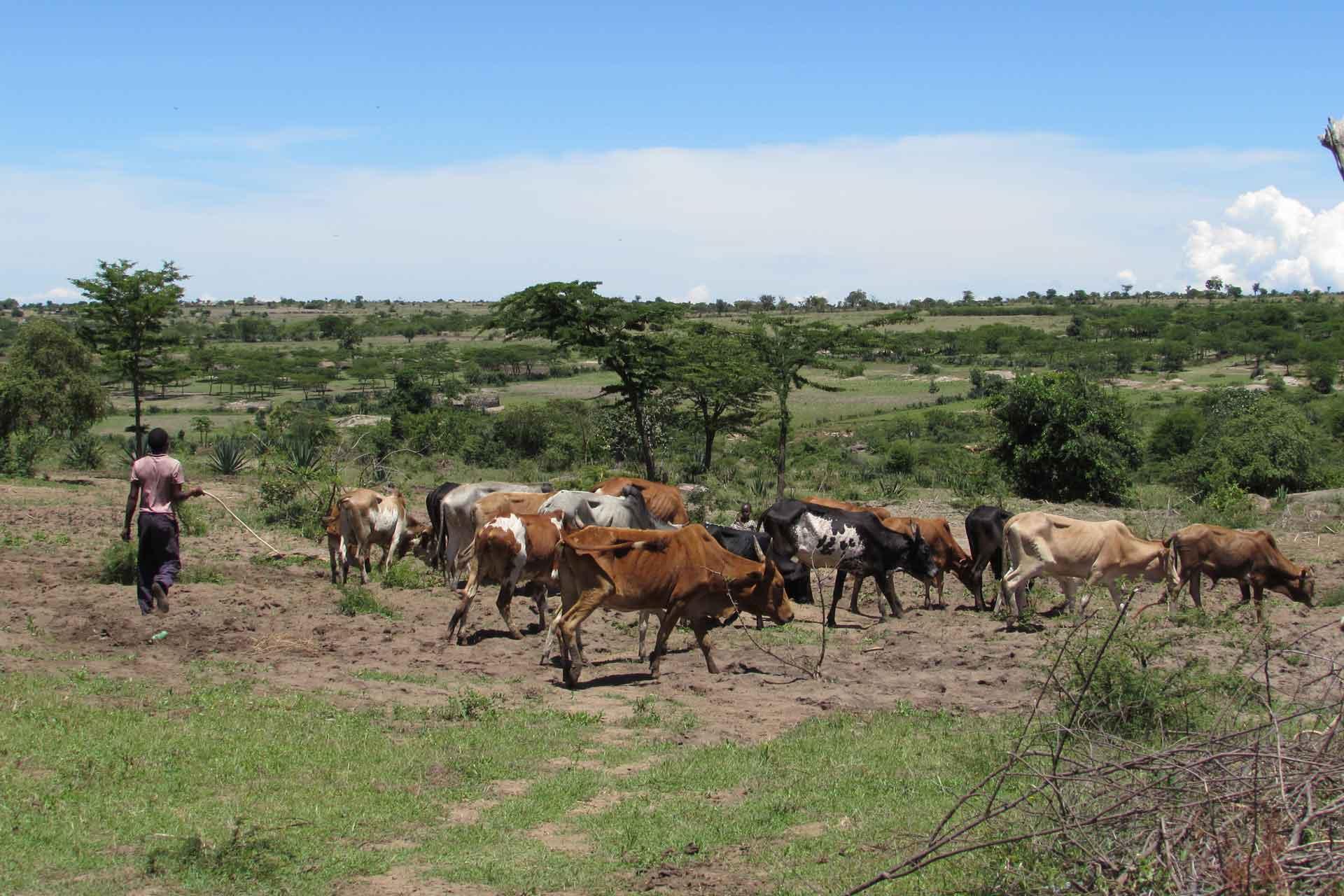
Understanding what shapes disease control: An historical analysis of foot-and-mouth disease in Kenya
Interpreting the interplay between politics, social demographics and epidemiology is essential for understanding how a disease's occurrence and control evolve over time. Foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) virus was first detected in Kenya in 1915 and serotyped in 1932. This review aims to describe and appraise initiatives to control FMD in Kenya since its independence from British rule in 1964, using information from the scientific literature. We describe the historical dynamics of FMD epidemiology in the country and determine socio-political factors that have shaped the control strategies used. PubMed, Scopus, CAB abstracts, Science Direct, Web of Science and Google Scholar were used to search and retrieve papers, using predetermined search criteria encompassing FMD, Kenya and disease control programme descriptors. In total 1234 papers were identified and screened for relevance using the World Health Organization's guidelines for rapid review. Ultimately 69 references from this search were included, and information extracted and consolidated. These papers highlight that following independence, there was a structured effort to control FMD consisting of a compulsory subsidised vaccination programme in the Rift Valley with movement controls and quarantine when outbreaks occurred. This programme led to an initial decrease in recorded FMD outbreaks. However, endemic circulation continued and this programme was discontinued due to multiple factors, including political deprioritisation and changes in the structure of veterinary services. Only low levels of active surveillance have been applied since 1964; most surveillance is passive and relies on outbreak reports. Currently control focuses on outbreak management and a mixture of public- and privately-funded vaccination. This review highlights critical drivers influencing disease control programme implementation including veterinary service structure, the active participation of stakeholders with farming systems and availability of affordable and matched FMD vaccine. Additionally, it appraises the availability of historical information and draws attention to gaps in the historical record.