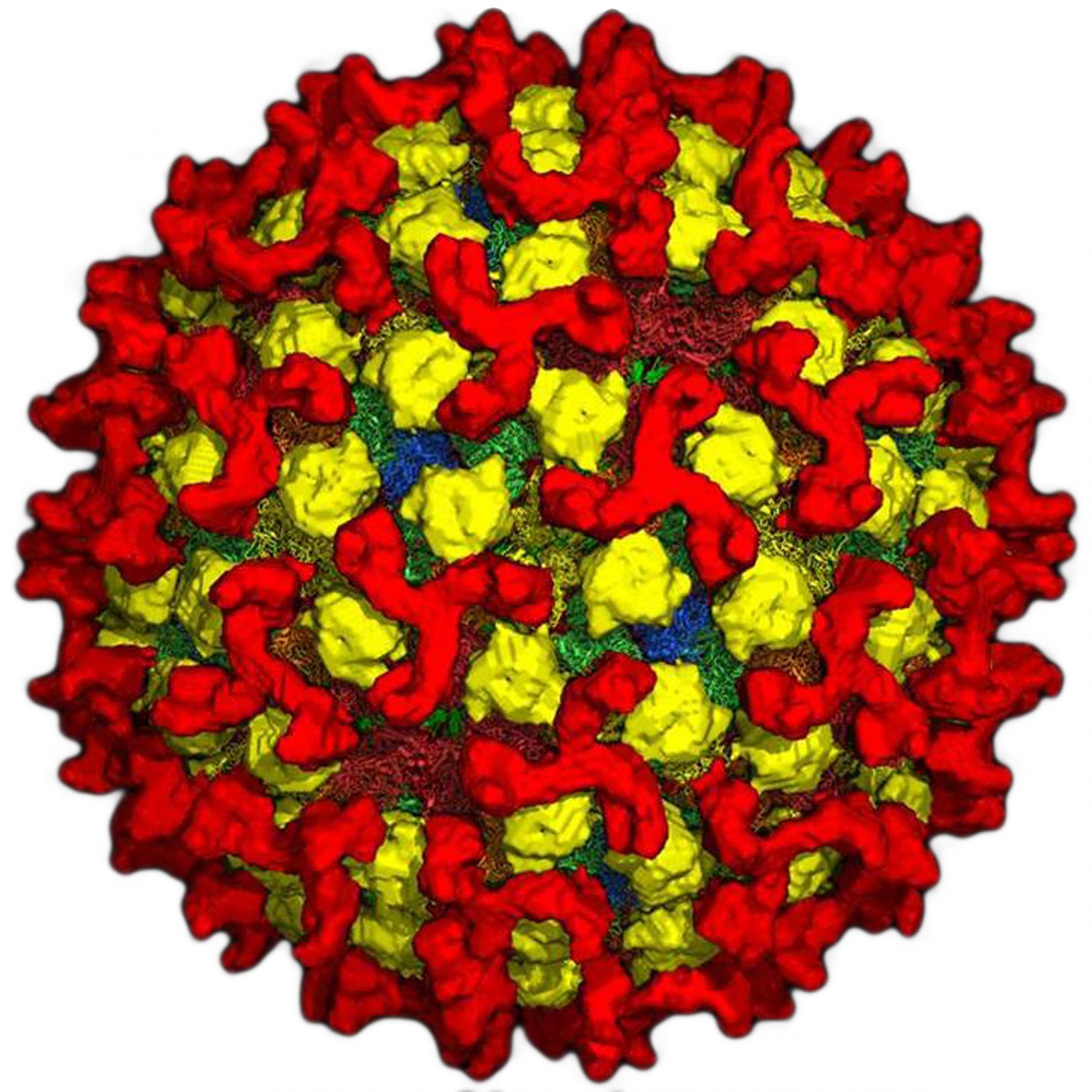
Capripoxvirus G-protein-coupled chemokine receptor: a host-range gene suitable for virus animal origin discrimination
The genus Capripoxvirus within the family Poxviridae comprises three closely related viruses, namely goat pox, sheep pox and lumpy skin disease viruses. This nomenclature is based on the animal species from which the virus was first isolated, respectively, goat, sheep and cattle. Since capripoxviruses are serologically identical, their specific identification relies exclusively on the use of molecular tools. We describe here the suitability of the G-protein-coupled chemokine receptor (GPCR) gene for use in host-range grouping of capripoxviruses. The analysis of 58 capripoxviruses showed three tight genetic clusters consisting of goat pox, sheep pox and lumpy skin disease viruses. However, a few discrepancies exist with the classical virushost origin nomenclature: a virus isolated from sheep is grouped in the goat poxvirus clade and vice versa. Intra-group diversity was further observed for the goat pox and lumpy skin disease virus isolates. Despite the presence of nine vaccine strains, no genetic determinants of virulence were identified on the GPCR gene. For sheep poxviruses, the addition or deletion of 21 nucleic acids (7 aa) was consistently observed in the 5? terminal part of the gene. Specific signatures for each cluster were also identified. Prediction of the capripoxvirus GPCR topology, and its comparison with other known mammalian GPCRs and viral homologues, revealed not only a classical GPCR profile in the last three-quarters of the protein but also unique features such as a longer N-terminal end with a proximal hydrophobic ?-helix and a shorter serine-rich C-tail.
Back to publications
Publication
Contributors
Le G C, Lamien C E, Fakhfakh E, Chadeyras A, Aba-Adulugba E, Libeau G, Tuppurainen E, Wallace D B, Adam T, Silber R, Gulyaz V, Madani H, Caufour P, Hammami S, Diallo A, Albina E
Year
2009
Journal
Journal of General Virology
Volume
90
Issue
8
Pages
1967-1977
Associated groups